

They are created when two different atoms share the same electron or when electrons travel from one atom to another.Įvery compound has certain features and a chemical formula. CompoundsĬompounds are groups of two or more elements that are tied together. In the 1950s the first atomic reactors were built. Later on scientists found out how this energy could be used in a peaceful way. The bombs released so much energy that they killed hundreds of thousands of people. We call this nuclear fission.įission was first used in atomic bombs that the Americans dropped over Japan to end the Second World War. In the 1930s and 40s scientists found out that if they bombarded a uranium atom with a neutron the nucleus would split up into two parts. In labs scientists can produce radioactivity by bombarding atoms with smaller particles. In nature, there are some elements that are radioactive, like uranium or radium. In some atoms the nucleus can change naturally. They have an electric charge.Ītoms that lose electrons become positive ions atoms that win electrons become negative ions. Atoms that gain or lose electrons are called ions. But it can gain or lose electrons when it crashes with other atoms. Normally, an atom is electrically neutral.
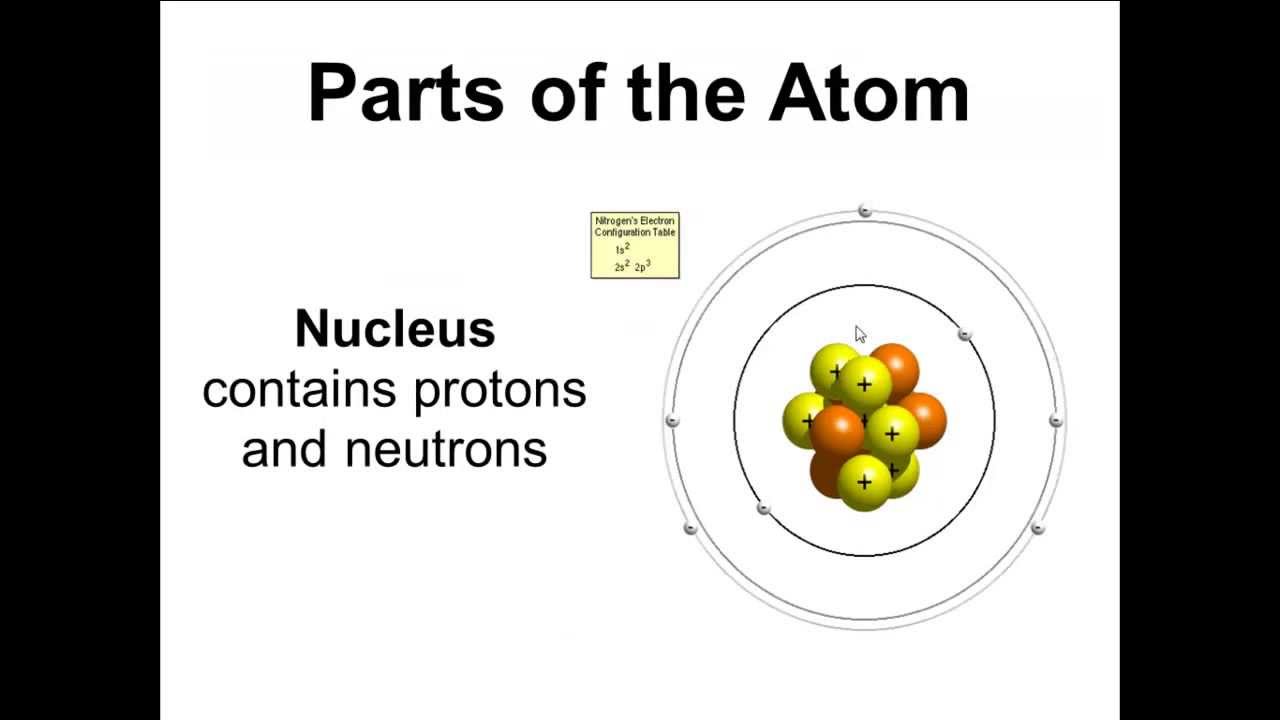
The atomic mass is never a whole number, because scientists do not just add protons and neutrons together. Uranium, for example has 92 protons and 146 neutrons. but heavier elements have more neutrons than protons. In most lighter elements the nucleus of each atom has the same number of protons and neutrons. Sometimes you can find hydrogen isotopes that have two or three neutrons, but they too have only one proton. Most of the time a hydrogen atom has one proton and one neutron. Such atoms are called isotopes.įor example, hydrogen has three isotopes. Although all atoms of the same element have the same number of protons, they sometimes have more neutrons. The atomic mass is the number of portions and neutrons in an atom. This table shows all the atoms in groups. The atomic number tells us where we can find an element in the periodic table. For example, every hydrogen atom has the atomic number 1 because it only has 1 proton.Įlements that have atomic numbers of up to 92 can be found in nature those over 92 are created by scientists in a laboratory. The atomic number tells you how many protons an atom has. The inner electrons travel fastest, the outer ones are the slowest.Įlectrons move around an atom in paths Properties of an Atom In most atoms, the outer shells are never completely filled with electrons. The second shell can hold 8, the third 18 and the fourth 32 electrons. The first shell is closest to the nucleus. If an electron has a lot of energy it moves around farther away from the nucleus.Įlectrons move around the nucleus in up to seven round paths, called shells. They want to break away from the nucleus. The energy of the nucleus keeps the electron inside the atom-just like the Earth keeps the moon in its orbit. In most cases an atom has the same number of protons and electrons. Each proton carries a positive electrical charge and each electron has a negative electrical charge. The parts of an atom have electrical charges.

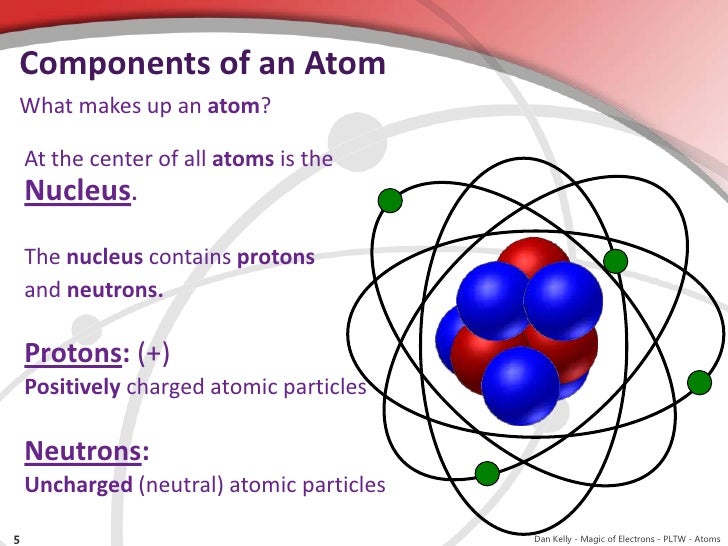
They have almost no mass and travel around the nucleus millions of times every second. The rest of the atom outside the nucleus is mostly empty.Įlectrons fly around in an atom very, very quickly. If an atom had a diameter of about 6 km the nucleus would only be as big as a tennis ball. It is very small if you compare it with the whole atom and it has almost all of an atom’s mass. Protons and neutrons are in the centre of an atom, which is called the nucleus. An atom consists of three parts : protons, neutrons, electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
